This is how our application simplifies the booking and administration process. Interested >>
Knee replacement surgery
Joint wear is one of the most common musculoskeletal problems, it is a widespread disease. Knee replacement surgery may become necessary if the desired improvement is not achieved by other treatments.
What causes joint wear?
Primary joint wear (primary arthrosis)
In this case, even the most thorough examinations cannot identify the cause of cartilage damage in the knee joint. Biological aging, degenerative changes, and a predisposition for it may play a great role in the development of the disease.
Secondary joint wear (secondary arthrosis)
In this case, the demise of the cartilage is caused by previous diseases.
Joint injuries, inflammations, rheumatological pathologies, fractures, deformities, congenital disorders, and previous surgeries.
What happens in the case of joint wear (arthrosis)?
- The hyaline cartilage wears out within the joint, it becomes uneven.
- Friction increases during movement.
- The internal lining of the joint capsule becomes inflamed by the detached pieces of cartilage.
- The production of joint fluid is increased, which leads to tightness.
- The joint’s range of motion is reduced due to the calcification.
- Movement and loading become painful.
What are the main symptoms of the disease?
- Pain that is characterized by the following:
- It develops after waking up in the morning, or when remaining in one position for a long period of time, then it is reduced after moving around a bit (pain at movement initiation).
- Increases on loading, or during longer walks.
- Decreases or abolishes at rest.
- Reduced walking ability and walking distance.
- Shortening of the limb.
- All of the above lead to limping.
What are the treatment options?
Basically, there are two types of treatment options available:
Non surgical (conservative) treatment
Aims:
- Reducing pain
- Increasing the joint’s range of motion
- Increasing muscle strength
- Decreasing limping
Methods:
- Pharmacological treatment:
- Anti inflammatory drugs
- Painkillers
- Antispasmodic drugs, relaxants
- Cartilage repair treatment
- Rheumatological treatments: physiotherapy, medical spa treatment (balneotherapy)
- Exercises enhancing the range of motion
Surgical treatment
The physician may recommend surgery if the non surgical treatment methods are no longer effective, and the diagnosis is confirmed by clinical examinations and X ray scans.
It is important to select the time of the intervention, which depends mostly on the patient’s pain tolerance, and the condition of the stabilizing musculature.
Types of surgeries which can be performed in case of knee arthrosis
- A cleansing and refreshment of the cartilage surface, drilling holes which provide nutrition to the soft tissues, and the transposition of bony cartilage islands (mosaicplasty), which could be performed with the surgical opening of the knee joint (arthrotomy), or an endoscopic procedure (arthroscopy). The latter may provide recovery in creating small, healthy surfaces. These methods may be used in special cases, based on individual evaluation. Even though a significant part of these surgeries does not provide a permanent solution, but a temporary improvement may be achieved with them which lasts for a few months, or maybe a few years.
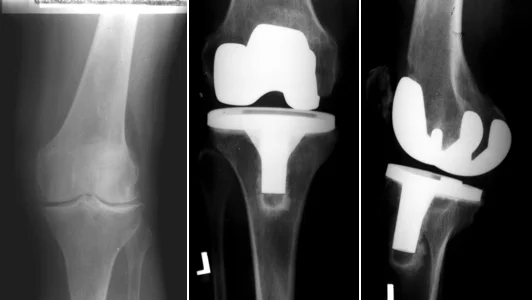
- The application of a unicompartmental or partial joint prosthesis means the replacement of the medial or the lateral side of the joint, on both the thighbone’s, as well as the shinbone’s side. This was an initial attempt, when the advent of knee prostheses arrived, and after this surgery, the replacement of the other side may become necessary after 1 5 years; this may necessitate repeated surgeries, or in a worse case, the removal of the original partial prosthesis, and the implantation of a total prosthesis, often in the form of revision. Currently, it is only recommended based on special indications.
- A total endoprosthesis means that the main loading areas of the knee joint, so the parts of the thighbone and the shinbone, are removed and replaced. The prosthesis is secured by bone cement and adequate molding. The part for the thighbone is made of metal, and the part for the shinbone is made of a metal plate, and a plastic liner. A stem may need to be placed in the medullary cavity of the bone if bone loss or major deformities are present. The surface of the kneecap is refreshed during surgery, the innervations are terminated by an electronic device.
- Kneecap replacement is a surgical procedure for cartilage damage, which affects the kneecap on its own, or it could also accompany a knee pathology, during which the kneecap is surgically removed, and a kneecap prosthesis is implanted with adhesives. This could be performed at the same time with a knee replacement surgery, or on its own too.
The surgical process of knee replacement
- The patient’s knee joint is explored from an incision that is made above the kneecap.
- The damaged joint surfaces are removed, then the place of the prosthesis is created on the thighbone and on the lower leg bone in a way that a prosthesis made of tissue friendly plastic and metal could be securely fixed with the help of bone cement.
- If only one half of the knee joint is affected, then only partial replacement; if both halves are affected, then complete replacement is performed.
- In one part of the cases, the joint surface of the kneecap is replaced too.
- Selecting the amount of bone tissue removed and the size of the prosthetic components allow that the axis of the knee joint, and the adequate tightness of the ligaments can be restored.
- One or two suction drains are inserted into the surgical site due to the accompanying postoperative bleeding.
- The wound is closed after thorough surgical hemostasis.
- Cover dressing and elastic bandage are applied.
What happens if the justified surgical treatment is not performed?
- The pain is expected to increase further.
- The movement disability may aggravate.
- The quality of life keeps deteriorating.
- The effectiveness of a surgery performed later may decrease.
We are pleased to announce that robotic surgery has been launched at our institution, the first step in the process being the introduction of robot-assisted knee replacement surgery supported by the CORI robotic system and artificial intelligence. The innovative procedure provides even greater precision and customization, as well as faster recovery time.
If you have any questions, please send a letter to magankorhaz@bhc.hu!







